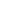
As a precision processing equipment, the long-term stable operation of hot stamping foil slitting machine depends on scientific design, reliability of key components and systematic maintenance management. The following are the key elements and maintenance points for stable operation:
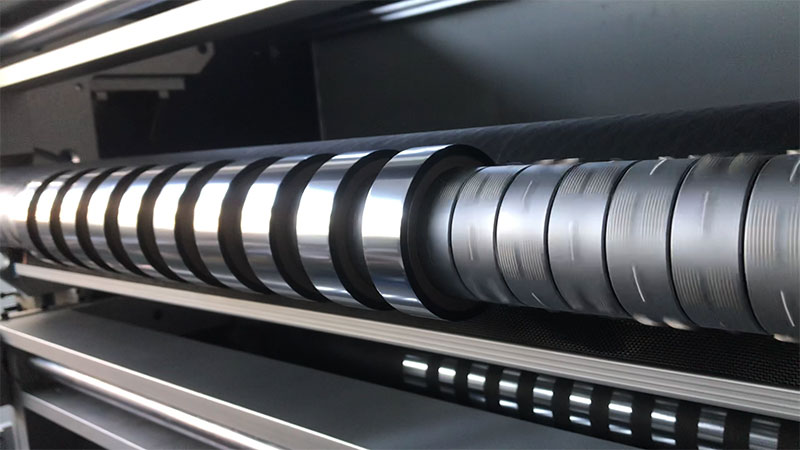

First, key components and stability guarantee
1. Slitting knife system
◦ Tool material: Tungsten carbide or coated tools (e.g. TiN coating) are used to ensure wear resistance and sharpness.
◦ Dynamic balance calibration: When rotating at high speed, it is necessary to ensure that the dynamic balance accuracy of the cutter shaft is ≤0.01mm, so as to avoid vibration causing burrs on the cutting edge.
◦ Temperature control: Install a cooling system (air-cooled/water-cooled) to prevent deformation at high temperature (recommended working temperature≤ 60°C).
2. Tension control system
◦ Closed-loop feedback: use high-precision magnetic powder brake + tension sensor (accuracy ± 0.1N), with PID algorithm for dynamic adjustment.
◦ Coil fitability: Preset tension parameters for different hot stamping foil materials (PET/OPP) to avoid stretching or wrinkling of the material.
3. Web Guiding System (EPC)
◦ Photoelectric detection: infrared or CCD sensor is used, and the detection accuracy needs to reach ±0.05mm.
◦ Actuator: Servo motor drives the correction roller, and the response time is < 20ms.
4. Transmission system
◦ High-precision gears/timing belts: Alloy gears with module ≥2, backlash checked regularly (standard ≤ 0.05mm).
◦ Bearing lubrication: NSK/SKF high-speed bearings are selected, and the grease is replenished every 500 hours (e.g. Shell Gadus S2 V220).
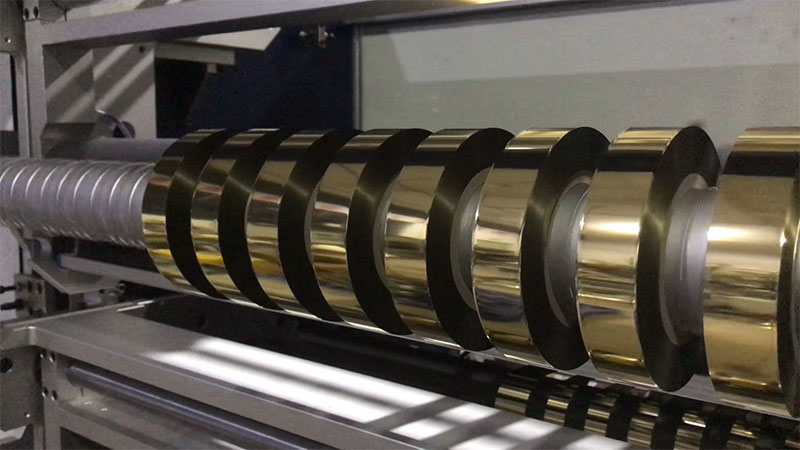
Second, the key points and cycle of maintenance
1. Routine maintenance
◦ Cleaning: Remove knife shavings and dust daily (use non-woven fabric + industrial vacuum cleaner) to prevent electrostatic adsorption.
◦ Tool inspection: Observe the cutting edge with a 20x magnifying glass, and replace the chipping edge ≥ 0.1mm immediately.
◦ Lubrication points: guide rails and lead screws are filled with ISO VG32 lubricating oil every day.
2. Periodic maintenance
◦ Weekly: Check the zero point of the tension sensor and check the air pressure (0.5~0.7MPa).
◦ Monthly: Detect the signal of the servo motor encoder and calibrate the reference position of the guiding system.
◦ Quarterly: Replace the hydraulic oil (ISO 46) and clean the tank filter (10 μm).
◦ Annual overhaul: dismantle the spindle to check the radial runout (allowable value≤0.005mm), and replace the aging seal.
3. Monitoring of key parameters
◦ Vibration monitoring: Install an accelerometer to warn when the vibration value > 2.5m/s².
◦ Temperature record: The bearing temperature exceeds 70°C and needs to be stopped for inspection.
◦ Section quality: Analyze the roughness of the section with an electron microscope regularly (Ra≤1.6μm is qualified).
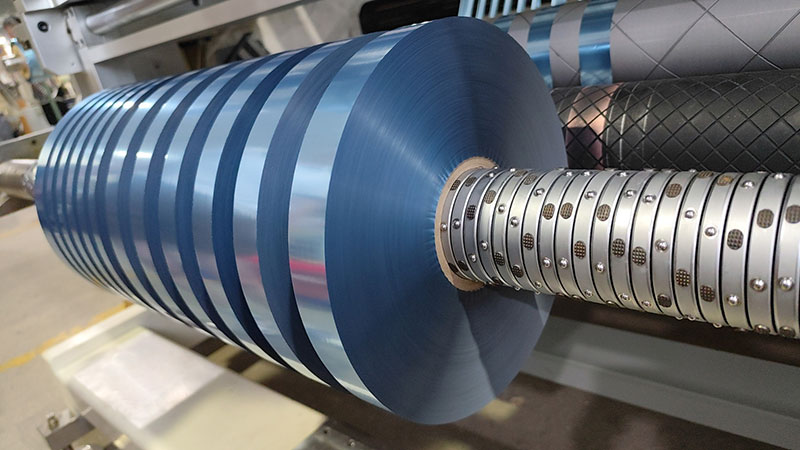
Third, common faults and countermeasures
| Fault phenomenon | Possible causes | solution |
| Sticky/burr trimmings | The tool is passivated or the temperature is too high | Change the tool and check the cooling system flow |
| Material misalignment | Contamination of the guiding sensor or insufficient air pressure | Clean the sensor and adjust the air pressure to 0.6MPa |
| The tension fluctuates greatly | Magnetic particle brake aging or PID parameter drift | Replace the magnetic particles and recalibrate the system |
Fourth, intelligent upgrade suggestions
1. Install PLC data acquisition module to record tool usage time, tension curve and other data in real time.
2. Introduce AI defect detection system (such as Halcon vision library) to automatically identify slitting defects and classify them.
3. Predictive maintenance technology is used to predict bearing life through vibration spectrum analysis.
Through the above measures, the MTBF (mean time between failures) of the hot stamping foil slitting machine can be increased to more than 4,000 hours, while reducing the cost of unplanned downtime by more than 30%. During maintenance, it is necessary to strictly follow the equipment manual, and adjust the maintenance cycle according to the actual working conditions.
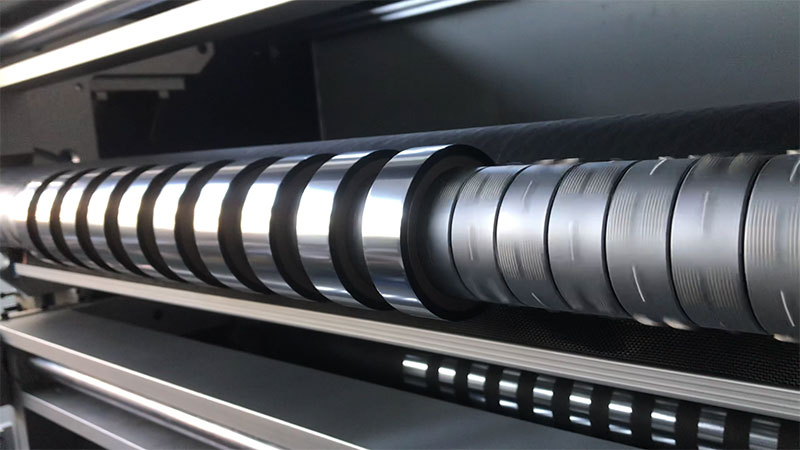
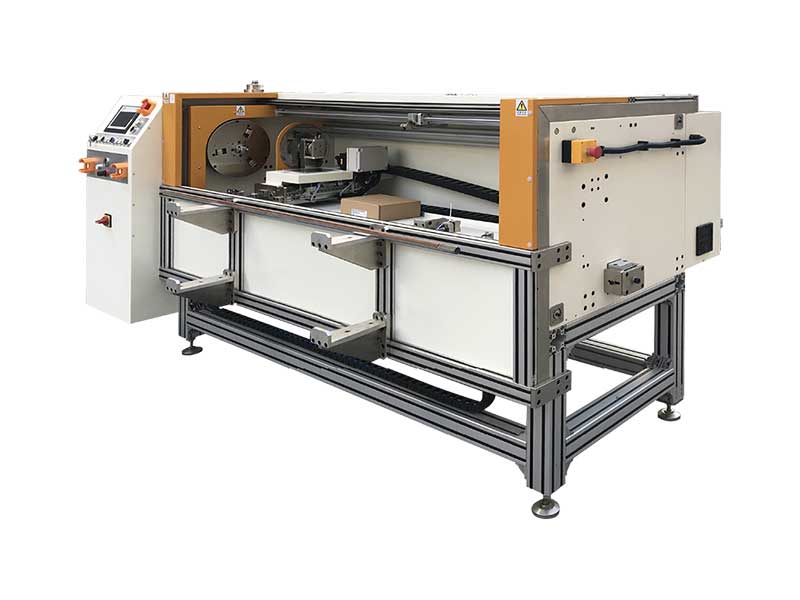




 Automatic Foil Roll Cutting Machine
Automatic Foil Roll Cutting Machine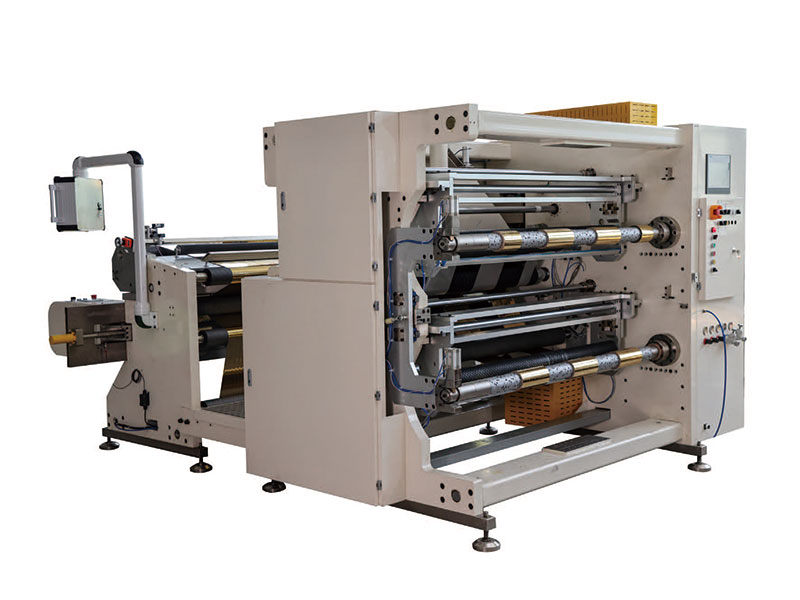 1400mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitting Machine
1400mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitting Machine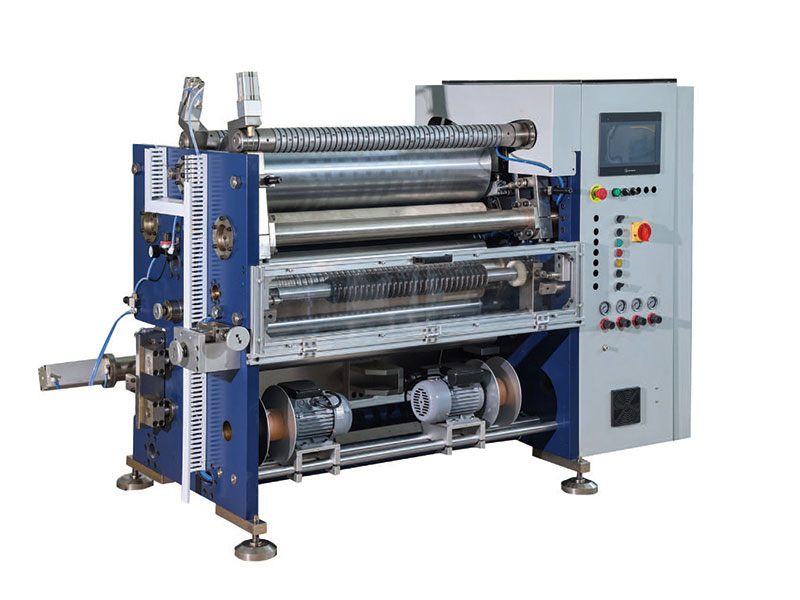 800mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitting Machine
800mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitting Machine 1350mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitting Machine
1350mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitting Machine Manual Foil Roll Cutting Machine
Manual Foil Roll Cutting Machine 1350mm/1600 Foil Slitting Machine
1350mm/1600 Foil Slitting Machine Photo & Card Print Ribbon Rewinding Machine
Photo & Card Print Ribbon Rewinding Machine 1400mm Copper Foil Slitting Machine
1400mm Copper Foil Slitting Machine