Introduction
As a key equipment in label printing, packaging and other industries, the operational safety of industrial ribbon slitting machine is directly related to production efficiency, product quality, and the personal safety of operators. A typical slitting machine involves multiple sources of risk during operation, such as high-speed rotating blades, precision tension control, high-temperature handling units (in some models) and electrical systems. This article will systematically explain the safety operation specifications of industrial ribbon slitting machines, aiming to provide a comprehensive and practical set of safety guidelines for operators and managers.

1. Safety preparation before operation
1.1 Personnel qualification and training
• Certified work: All operators must undergo professional training and pass the assessment, and be familiar with the equipment structure, working principle and emergency handling procedures
• Regular retraining: Conduct safety operation retraining every six months to understand the safety features of the equipment after the update
1.2 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
• Necessary equipment: cut-resistant gloves, protective glasses, tight overalls, non-slip safety shoes
• Special situations: dust masks should be worn when handling special materials, and people with long hair must wear work caps
1.3 Device status check
• Mechanical inspection: Confirm that the blade is securely installed without loosening, the transmission parts are well lubricated, and the safety shield is intact
• Electrical inspection: Check that the emergency stop button is functioning normally, the grounding line is intact, and there is no abnormal alarm in the control system
• Environmental inspection: Ensure that the work area is adequately lit, the ground is dry and free of oil, and the fire escape is unobstructed

2. Safety operation procedures during operation
2.1 Loading and strapping procedures
1. Feeding preparation: Confirm that the machine is completely stopped, press the emergency stop button before loading operation
2. Material inspection: Check whether the ribbon coil is damaged or deformed to avoid fractures during operation and cause danger
3. Standardize the threading: Strictly follow the belt path specified in the equipment manual to avoid material deviation or entanglement
2.2 Parameter setting and debugging
1. Start at low speed: After the initial setting, test run at the lowest speed, and gradually increase the speed after confirming that there are no abnormalities
2. Tension control: Set the appropriate tension according to the ribbon type and width to avoid over-tight breakage or over-loose folds
3. Temperature control: If the equipment contains a hot cutting unit, it needs to be preheated to a set temperature and stabilized before starting production
2.3 Key points of operation monitoring
• Continuous observation: Operators need to monitor the operation status of the equipment throughout the process and must not leave their posts without authorization
• Abnormal Identification: Pay attention to abnormal sounds, vibrations, or odors, and stop the machine immediately for inspection
• Cleaning Specifications: It is strictly forbidden to clean the blade area or touch moving parts during operation

3. Safety management of special operating situations
3.1 Blade Replacement and Maintenance
1. Complete power outage: The main power supply must be cut off and a "repairing" warning sign must be hung before replacing the blade
2. Professional Tools: Use specialized tools to remove the blades, and use alternative tools is strictly prohibited
3. Blade handling: Scrapped blades should be placed in special containers to avoid accidental cuts
3.2 Emergency handling
• Sudden Shutdown: Immediately press the red emergency stop button to record the operating parameters during the shutdown
• Material blockage: Completely shut down and confirm blade stop before processing blocked material
• Electrical faults: Inspected and dealt with by professional electricians, and non-professionals are strictly prohibited from disassembling the electrical box
3.3 Replacement and specification adjustment
1. Full Shutdown: Any specification adjustments must be made in complete downtime
2. Parameter review: After adjustment, two people need to review the key parameters (width, tension, speed)
3. Test cut verification: Use scrap materials for trial cutting, and then put into formal production after confirming that it is correct

4. Specifications for the use of safety protection systems
4.1 Physical protective devices
• Protective Covers: Ensure that all protective shields are closed and locked during operation
• Grating Protection: Regularly test the sensitivity of the photoelectric protection device to ensure effectiveness
• Interlocks: It is strictly forbidden to short-connect or bypass any safety interlocks
4.2 Electrical safety system
• Emergency Stop: Familiarize yourself with all emergency stop button positions to ensure that you can reach them within 1 second
• Overload protection: Understand the overload protection characteristics of the equipment and do not adjust the set value arbitrarily
• Leakage Protection: Test the leakage protector monthly to ensure proper functioning
4.3 Safety signage system
• Identification Signs: Familiarize yourself with the meaning of all safety warning signs on your device
• Status Indication: Understand the color meaning of various indicators (run, fault, standby).
• Restricted area signs: strictly abide by the restricted area area marked by the yellow and black warning lines around the equipment

5. Maintain safety norms
5.1 Daily maintenance
• Safe to clean: Use specialized tools to clean and avoid direct contact with the blade edge
• Lubrication specifications: Use the specified lubricating oil as required by the manual to avoid contaminating the ribbon
5.2 Regular maintenance
• Maintenance plan: Formulate and strictly implement the regular maintenance schedule
• Complete records: Detailed records of each maintenance, replacement parts and problems found
• Functional testing: After maintenance, all safety functions are fully tested and confirmed to be normal before putting them into use

6. Safety management system construction
6.1 Safety responsibility system
• Clarify responsibilities: establish a three-level safety responsibility system for operators, team leaders, and safety specialists
• Shift handover system: Strictly implement the safety status handover system and record the safety status of equipment
6.2 Safety inspection and improvement
• Daily inspection: Conduct a 5-minute safety inspection before operation and fill in the inspection form
• Hidden danger investigation: Conduct a systematic safety hazard investigation once a week
• Continuous improvement: Establish a safety suggestion feedback mechanism to encourage all employees to participate in safety improvement
6.3 Emergency preparedness
• Emergency plan: Formulate emergency plans for fire, electric shock, mechanical injury, etc
• Emergency drills: Organize emergency drills every quarter to improve actual combat capabilities
• First Aid Facilities: Ensure that the work area is fully equipped with a first aid kit and that relevant personnel are equipped with basic first aid skills
Epilogue
The safe operation of industrial ribbon slitting machine is not a single technical problem, but involves equipment management, personnel training, system construction and other aspects of system engineering. Only by internalizing safety awareness into daily habits and implementing safety specifications into every operational detail can we truly achieve the production goal of "zero accidents". Enterprises should continue to invest resources to improve safety facilities, strengthen personnel training, build a safety culture based on prevention, and build a protective wall for every operator while improving production efficiency.
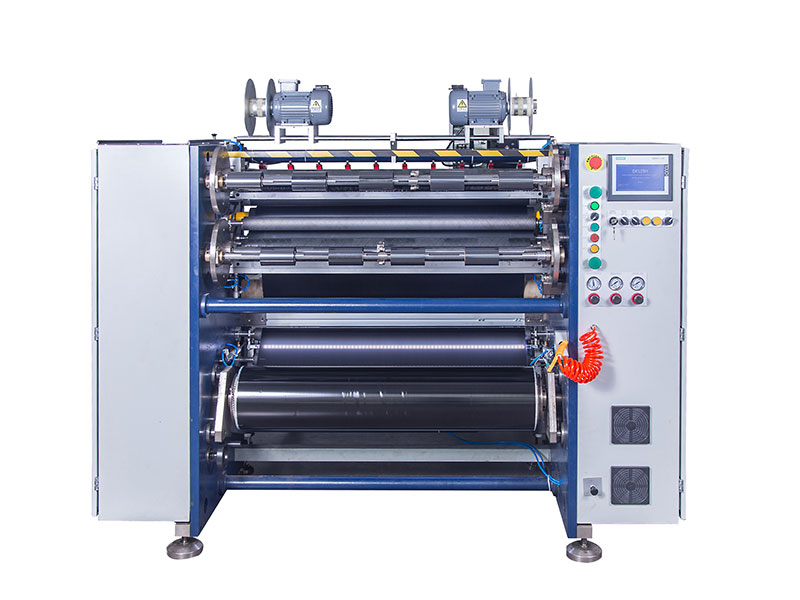
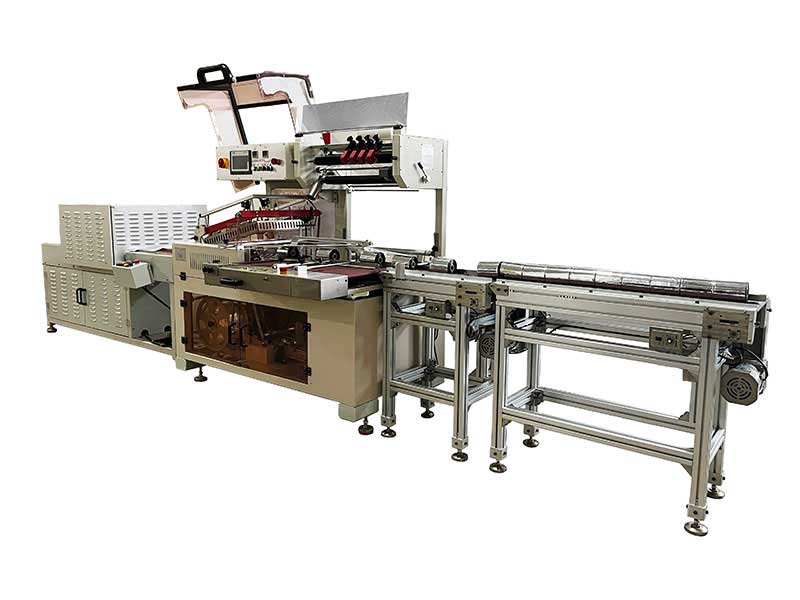







 Thermal Transfer Ribbons Packaging Machine
Thermal Transfer Ribbons Packaging Machine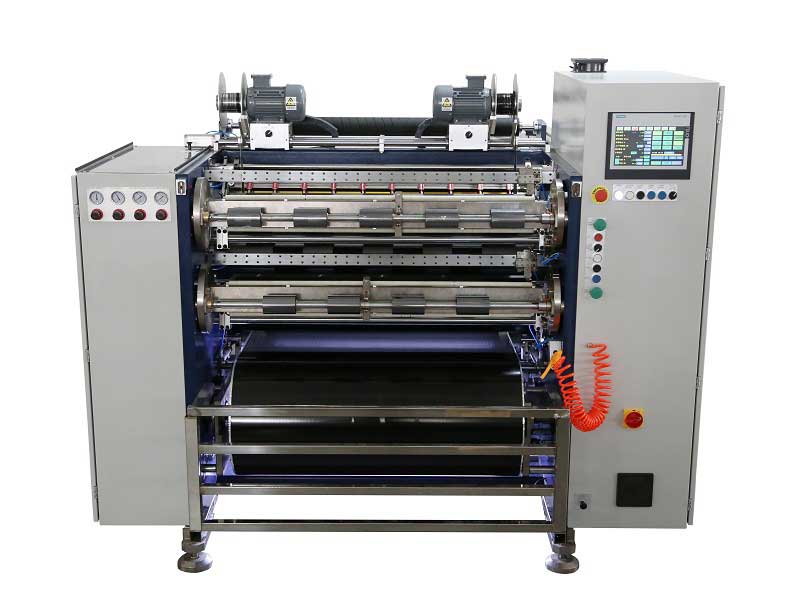 Automatic Thermal Transfer Ribbon Slitting Machine RSDS8 H PLUS
Automatic Thermal Transfer Ribbon Slitting Machine RSDS8 H PLUS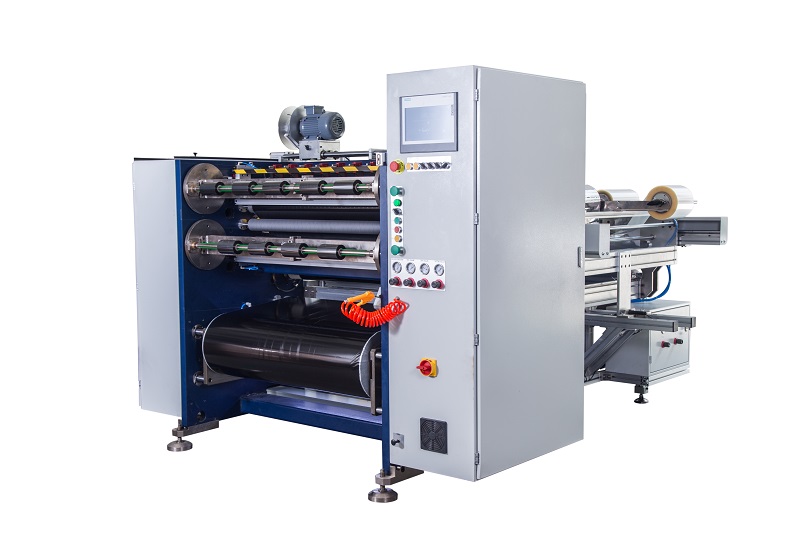 Semi Automatic Thermal Transfer Ribbon Slitting Machine RSDS5 PLUS
Semi Automatic Thermal Transfer Ribbon Slitting Machine RSDS5 PLUS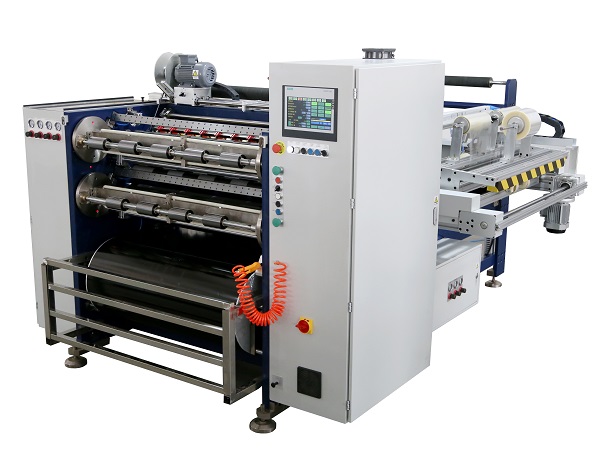 Automatic Thermal Transfer Ribbon Slitting Machine RSDS8 PLUS
Automatic Thermal Transfer Ribbon Slitting Machine RSDS8 PLUS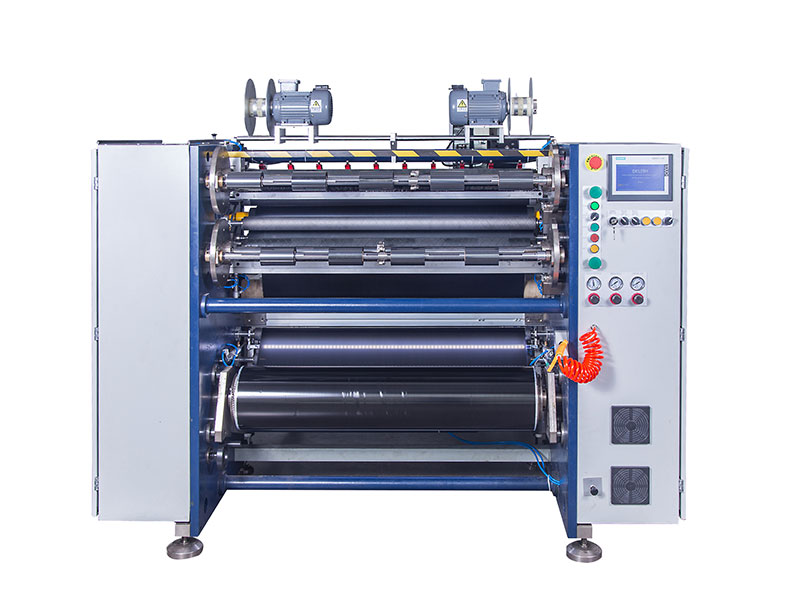 Ribbon Slitting Machine
Ribbon Slitting Machine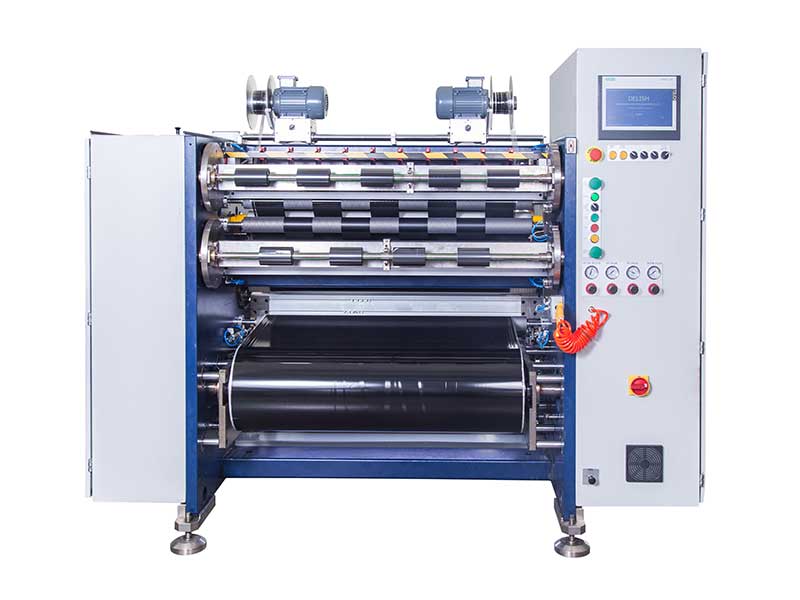 TTR Slitting Machine
TTR Slitting Machine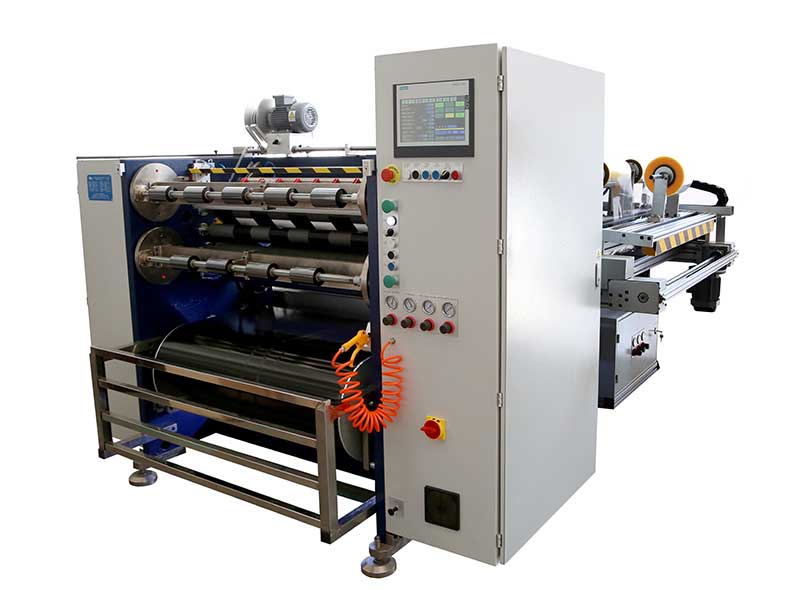 Automatic Thermal Transfer Ribbon Slitting Machine RSDS6 PLUS
Automatic Thermal Transfer Ribbon Slitting Machine RSDS6 PLUS