The application of hot stamping foil slitting machine in the packaging industry mainly improves the utilization rate, reduces costs and meets the diversified process needs through precise slitting of hot stamping materials (hot stamping foil foil). The following are its core application values and technical points:
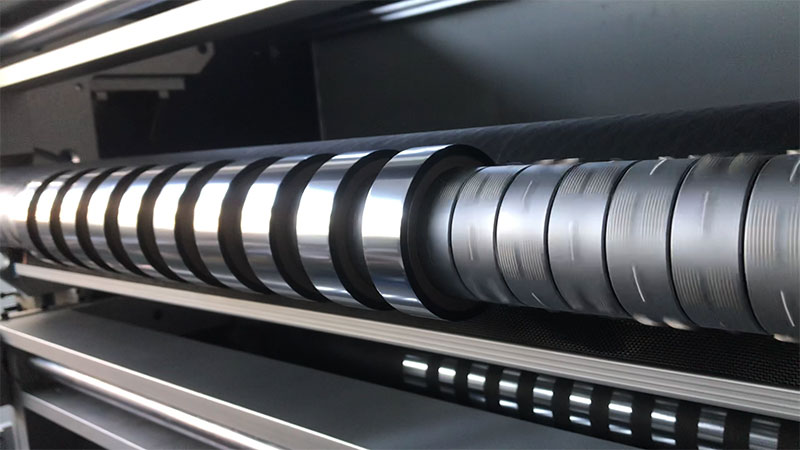

1. Key technologies to improve material utilization
• High-precision slitting: CNC or laser positioning technology is used to cut the wide hot stamping foil foil into specific widths (such as 1mm to 1000mm) to reduce edge waste and adapt to the needs of hot stamping area of different packaging products.
• Reduce joint loss: automatic slitting avoids the misalignment waste in traditional manual cutting, and the material utilization rate can be increased by 15%-30%.
• Residual material recovery design: Some slitting machines integrate a scrap material recovery system to rewind the narrow residual material after slitting.
2. Specific application scenarios in the packaging industry
• Customized packaging for small batches: The slitting machine flexibly adjusts the width of hot stamping foil to meet the hot stamping needs of small batch orders such as gift boxes and labels, and avoid the waste of wide materials.
• Complex pattern foil stamping: Slitting narrow strips of hot stamping foil is used for fine patterns (such as logo, text), which saves material compared to overall hot stamping.
• Multi-material adaptation: For different packaging materials such as paper, plastic, leather, etc., slitting hot stamping foil with corresponding characteristics (such as high temperature resistance and high adhesion type).
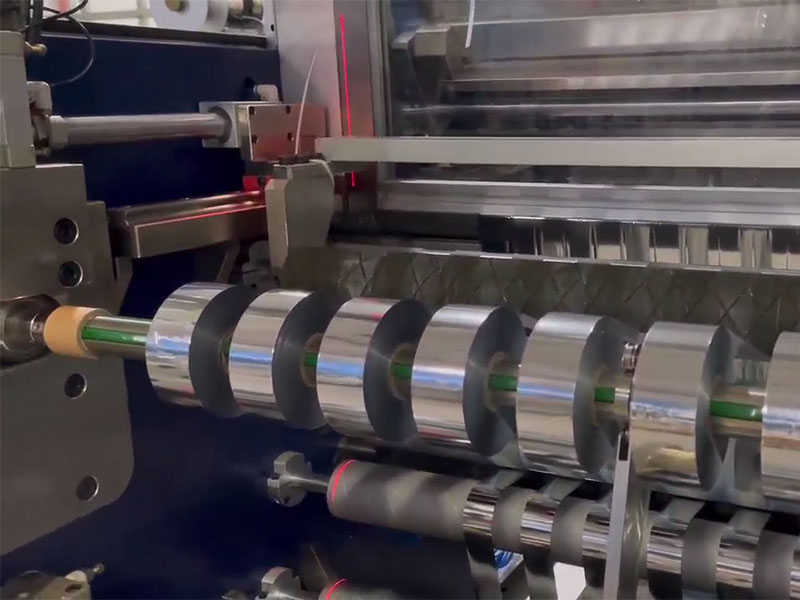

3. Automation and intelligent upgrading
• Intelligent deviation correction system: real-time monitoring of slitting position through photoelectric sensors to ensure slitting accuracy (±0.1mm) and reduce scrap rate.
• Data control: Connect to the MES system, automatically calculate the optimal slitting scheme according to the order requirements, and dynamically adjust the parameters (such as tension and speed).
• Quick mold change technology: The modular design supports quick replacement of the cutter spindle, adapts to the needs of multi-specification slitting, and reduces downtime.
4. Economic benefit analysis
• Direct cost savings: material utilization increased from 60% to more than 85%, significantly reducing the cost of hot stamping (20%-40% of the packaging process cost).
• Hidden benefits: reduce the frequency of roll changes, reduce storage pressure (narrow rolls are easier to store), and improve the efficiency of the hot stamping process.
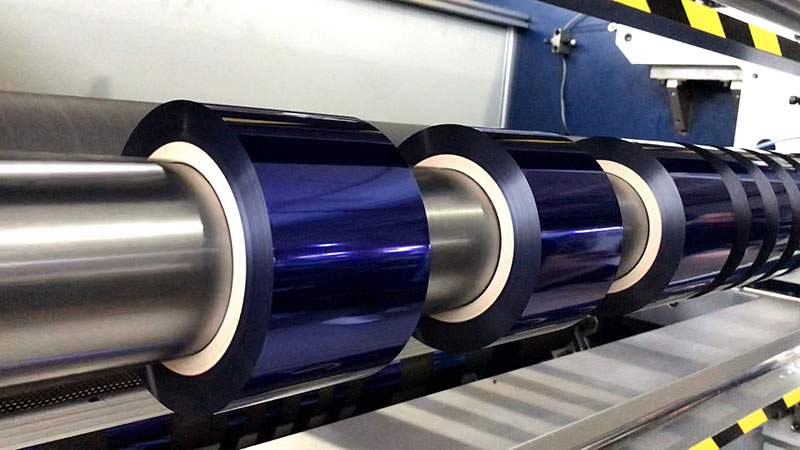

5. Future development trends
• Green slitting technology: research and development of low-energy slitting equipment, with degradable hot stamping foil foil, to respond to the demand for environmentally friendly packaging.
• AI optimization algorithm: Through historical data learning, it automatically recommends the combination of slitting parameters to further reduce the loss of trial and error.
Case Reference
After the introduction of CNC slitting machine in a high-end liquor packaging factory, the waste rate of hot stamping foil was reduced from 25% to 8%, saving more than 1.2 million yuan in annual material costs, and the rate of defective bronzing products decreased by 50%.
Through the precise processing of the slitting machine, packaging enterprises can reduce costs and increase efficiency while improving the hot stamping effect, especially suitable for high-end packaging fields that are sensitive to process fineness and cost.
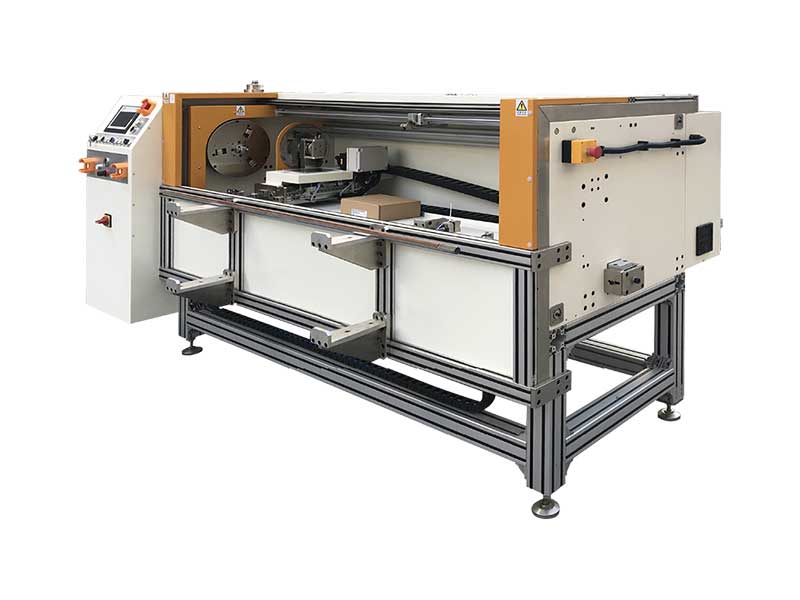


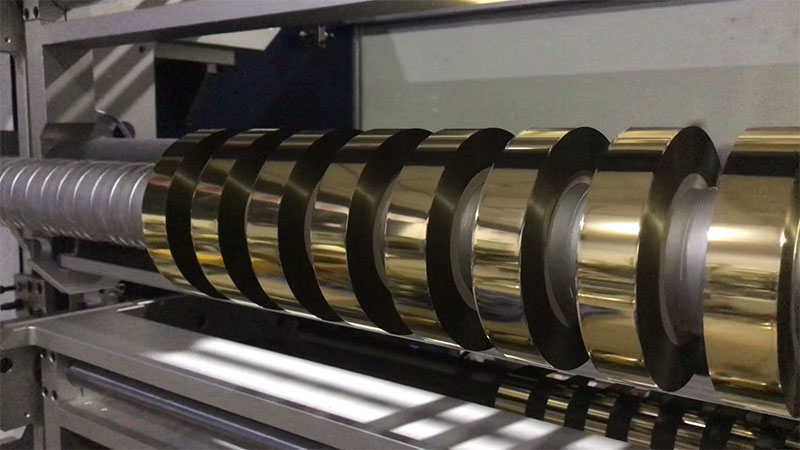

 Automatic Foil Roll Cutting Machine
Automatic Foil Roll Cutting Machine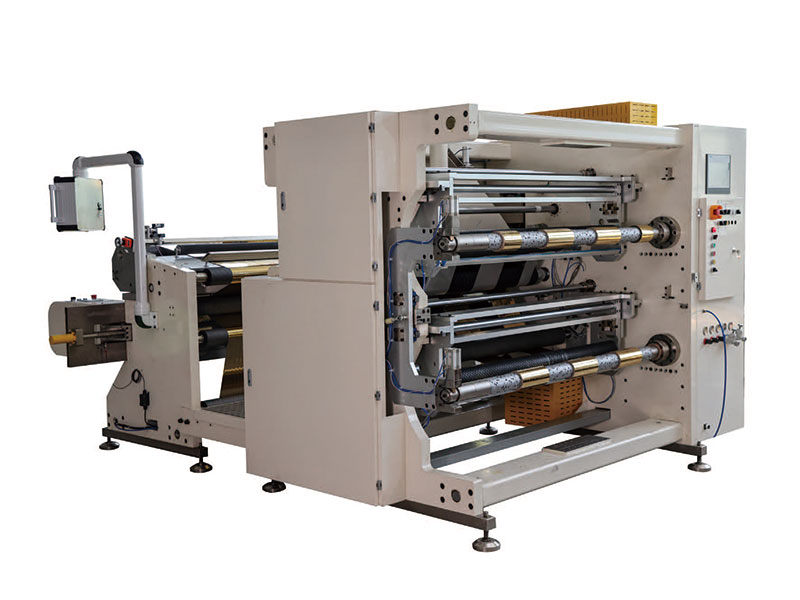 1400mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitting Machine
1400mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitting Machine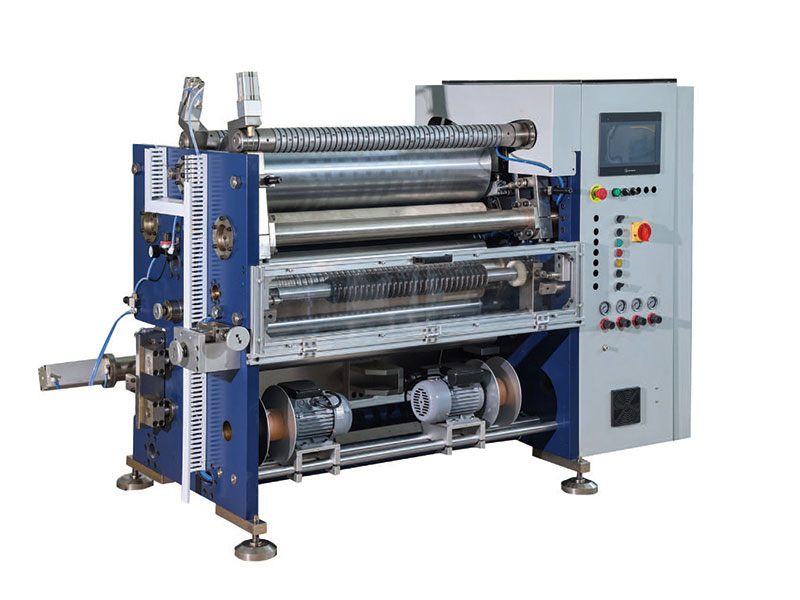 800mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitting Machine
800mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitting Machine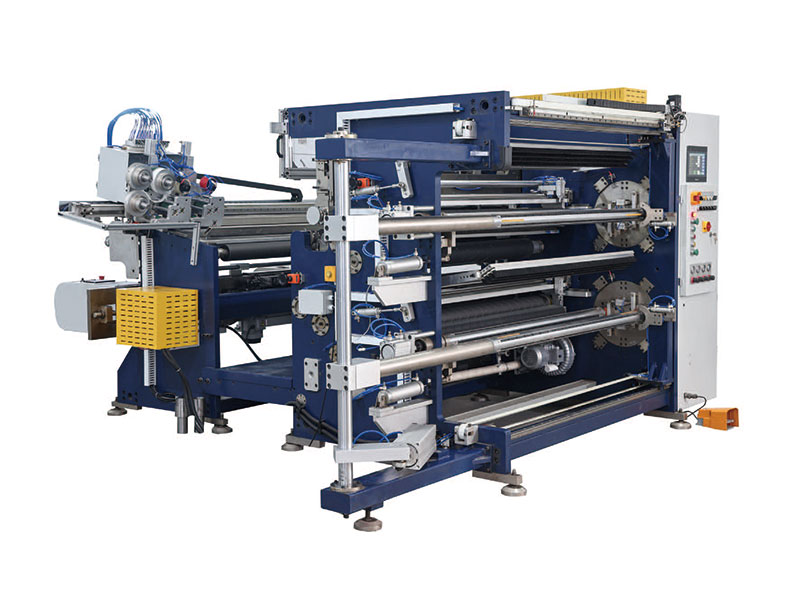 1350mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitting Machine
1350mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitting Machine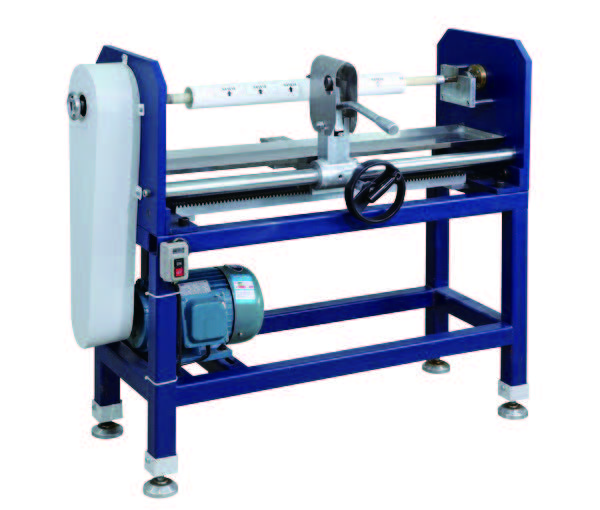 Manual Foil Roll Cutting Machine
Manual Foil Roll Cutting Machine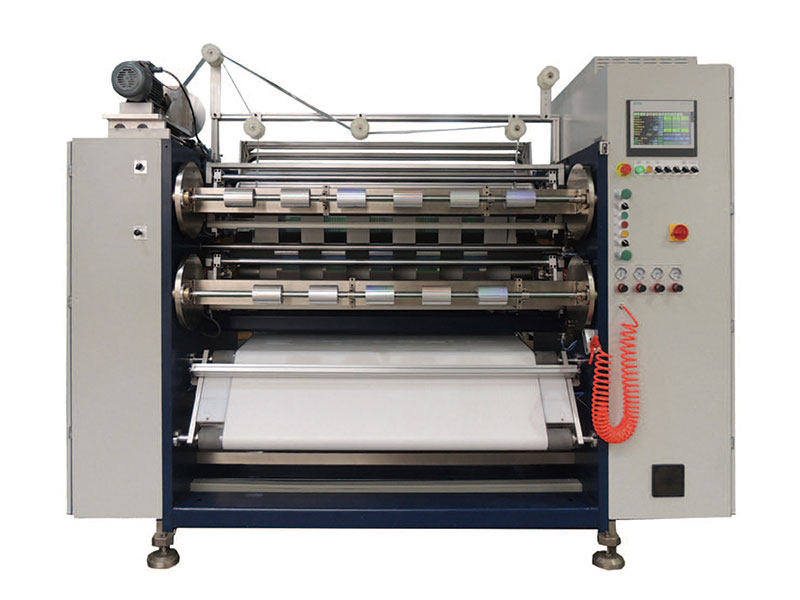 1350mm/1600 Foil Slitting Machine
1350mm/1600 Foil Slitting Machine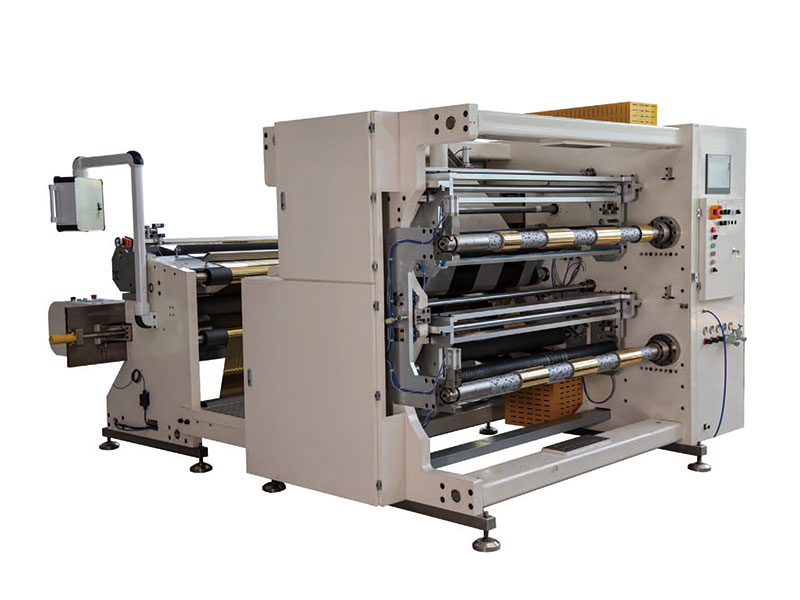 1400mm Copper Foil Slitting Machine
1400mm Copper Foil Slitting Machine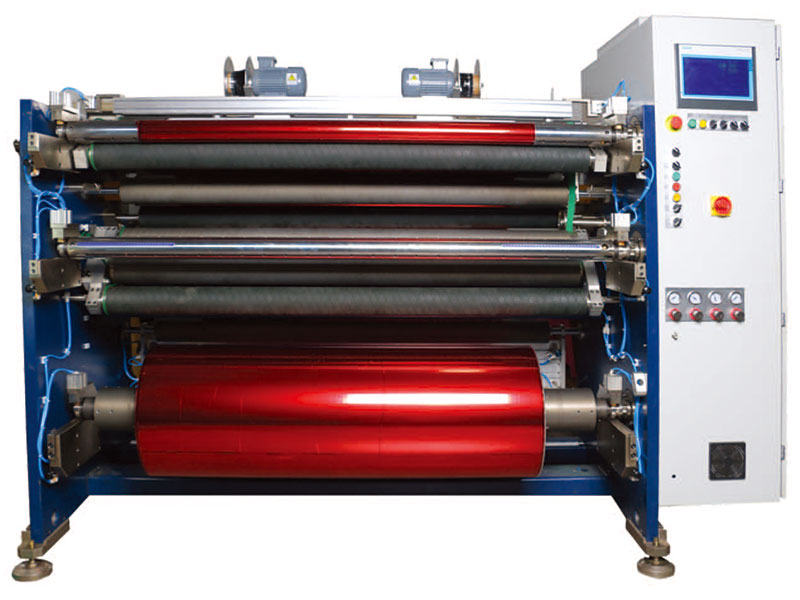 1600mm Foil Slitting Machine
1600mm Foil Slitting Machine