In the slitting process of ultra-thin agricultural films (usually 5-20 μm thick), the accuracy and stability of the tension control system directly determine the slitting quality, material utilization rate and production efficiency. Due to the characteristics of extremely thin thickness, high ductility and easy stretch deformation, improper tension control will lead to wrinkling, delamination, uneven edges and even fracture of the film. The following are the key roles and optimization directions of the tension control system in the slitting of ultra-thin agricultural films:
First, the harm of uncontrolled tension to the slitting of ultra-thin agricultural film
1. Excessive tension
◦ The film is stretched and deformed, resulting in uneven thickness (affecting agricultural properties such as light transmittance and heat retention).
◦ The winding is too tight, the film layers are adhered to each other, and it is difficult to unfold when used (commonly known as "dead roll").
◦ The stress at the edge is concentrated, and the film roll appears "chrysanthemum pattern" or tendon after slitting.
2. The tension is too low
◦ The film roll is relaxed, the lateral deviation is deviated, and the slitting width accuracy decreases.
◦ The winding is not neat, the end face is uneven, and the roll is easy to collapse during transportation.
◦ The film slips with the guide roller, resulting in electrostatic adsorption of impurities.
3. Tension fluctuations
◦ Abrupt changes in tension during slitting (e.g., acceleration/deceleration phases) that cause periodic wrinkles or stretch marks on the membrane surface.

Second, the core requirements of slitting tension control of ultra-thin agricultural films
1. High-precision control
◦ Tension fluctuations should be controlled within ±0.5% (usually ±2% for ordinary films).
◦ Dynamic response time < 10ms to avoid tension lag when speed changes.
2. Multi-stage collaborative control
◦ The slitting machine needs to realize independent control of the tension of the three stages of unwinding, traction and rewinding, and the transition is smooth.
◦ Unwinding adopts taper tension control (automatically reduces the tension with the decrease of the roll diameter to prevent the inner layer from being extruded and deformed).
3. Anti-interference ability
◦ Overcome interference factors such as uneven film thickness, electrostatic adsorption, and changes in ambient temperature and humidity.
Third, the key technical scheme of the tension control system
1. Hardware configuration optimization
• High sensitivity sensor
◦ Magnetic particle brake/clutch + tension sensor closed-loop control, detection accuracy up to 0.1N.
◦ Or use a sensorless tension estimation algorithm (which pushes the tension back from the motor current to reduce mechanical delay).
• Servo drive system
◦ The winding and unwinding motor selects servo motor + high-precision encoder to realize seamless switching of torque/speed dual mode.
• Elastic roller compensation device
◦ Floating rollers are installed in the traction section to buffer tension fluctuations in real time through displacement sensors.
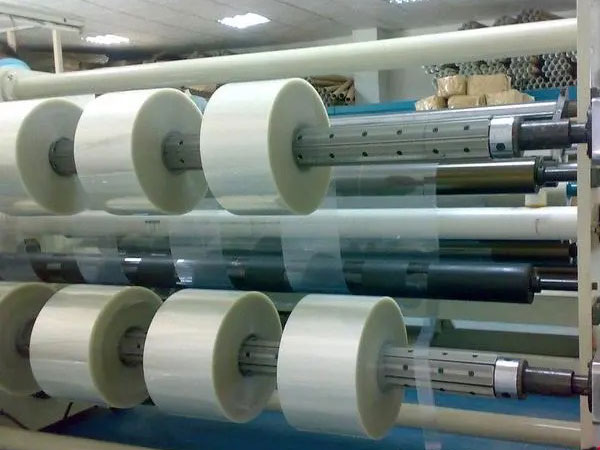

2. Control policy upgrade
• PID algorithm improvements
◦ Fuzzy adaptive PID is used to adjust parameters (e.g., integration time) according to the change of membrane diameter and speed.
◦ Introduced feedforward control to predict the effects of inertia during acceleration/deceleration.
• Application of modern control theory
◦ Model Predictive Control (MPC): Establish a mathematical model based on the material properties of thin films to optimize the dynamic response.
◦ Neuronal network control: Learn the optimal tension curve under complex operating conditions from historical data.
3. Process auxiliary measures
• Static Elimination
◦ Install ionizing air bars to reduce tension abrupt changes caused by thin film adsorption guide rollers.
• Constant temperature and humidity in the environment
◦ Control the temperature and humidity of the workshop (such as 25±2°C, RH50±5%) to avoid the hygroscopic expansion of the film affecting the tension stability.
• Surface treatment of guide rollers
◦ Use ceramic-coated guide rollers or rubber-coated rollers to adjust the coefficient of friction to match the characteristics of the film.
4. Analysis of typical cases
• Transformation effect of an agricultural film enterprise:
◦ Original equipment: Mechanical tension control, 12% scrap rate when slitting 8μm film.
◦ After transformation: servo motor + fuzzy PID control, tension fluctuation ± 0.3%, the rejection rate is reduced to less than 2%, and the annual cost of film material is saved by more than 800,000 yuan.
• High-speed slitting scenario (linear speed>600m/min):
Using MPC algorithm + sensorless detection, the tension stability is increased by 40% to meet the needs of high-speed slitting.
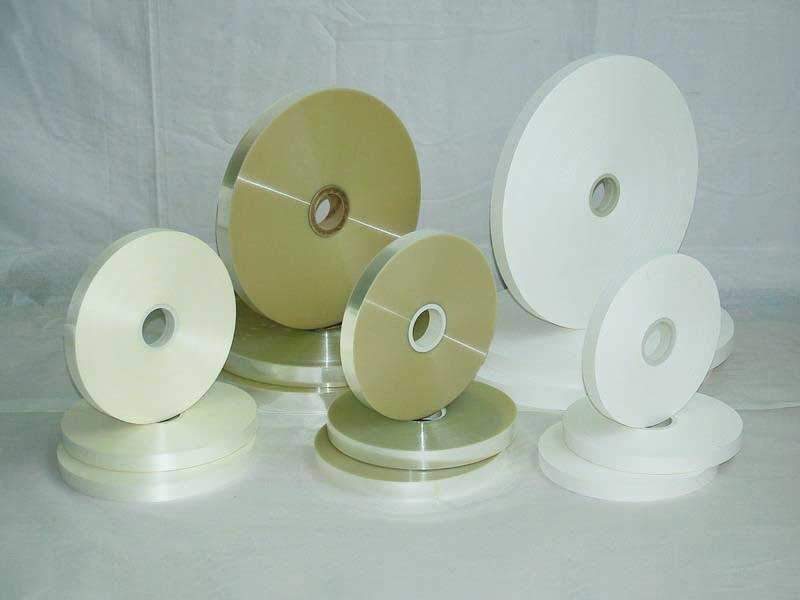

Fifth, the future development trend
1. Digital twin technology
◦ The slitting process is rehearsed through virtual simulation, and the tension parameters are optimized before actual production.
2. AI real-time optimization
◦ Visual inspection of film surface defects and reverse adjustment of tension setpoints.
3. All-in-one integration
◦ The tension control system is deeply integrated with the main control PLC and MES system of the slitting machine to realize the data traceability of the whole process.
summary
The tension control of ultra-thin agricultural film slitting is a "balancing art of precision and flexibility", which requires a combination of high-response hardware, intelligent algorithms and process experience. Companies should prioritize upgrading servo drives and sensor systems, and customizing parameters through material property testing (e.g., modulus of elasticity, coefficient of friction) to achieve high-quality, low-loss slitting production.
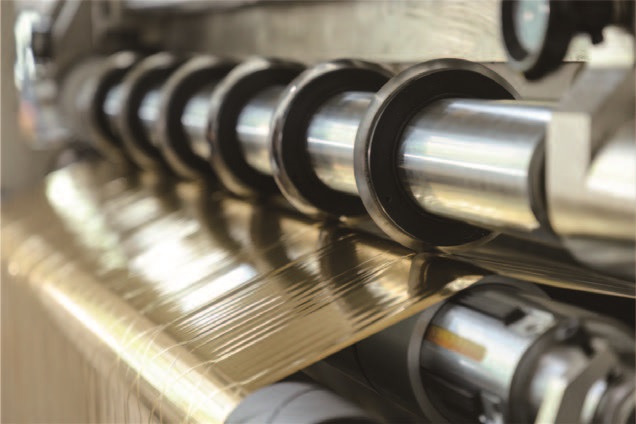
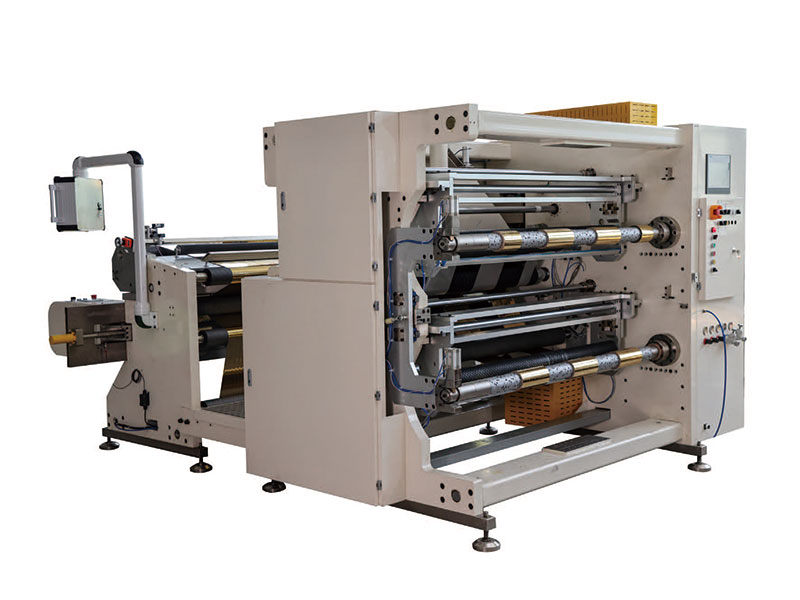





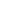
 1400mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitting Machine
1400mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitting Machine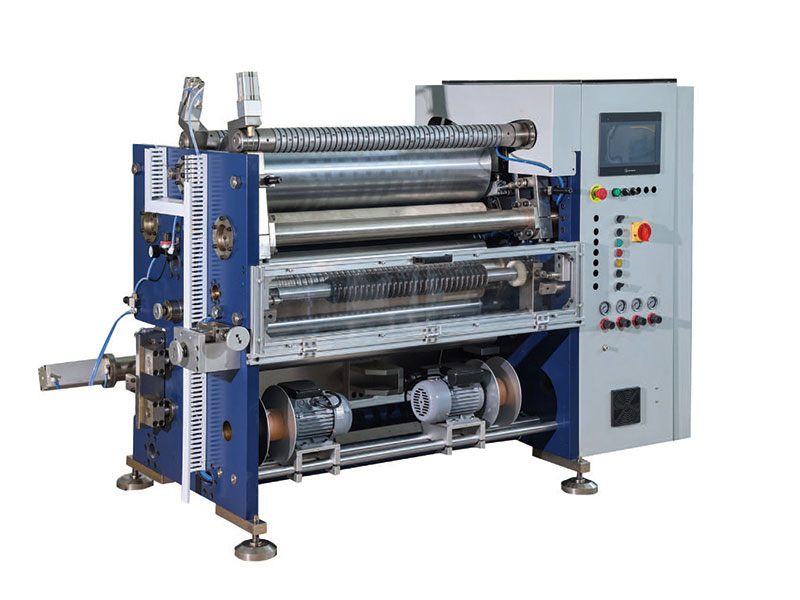 800mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitting Machine
800mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitting Machine 1350mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitting Machine
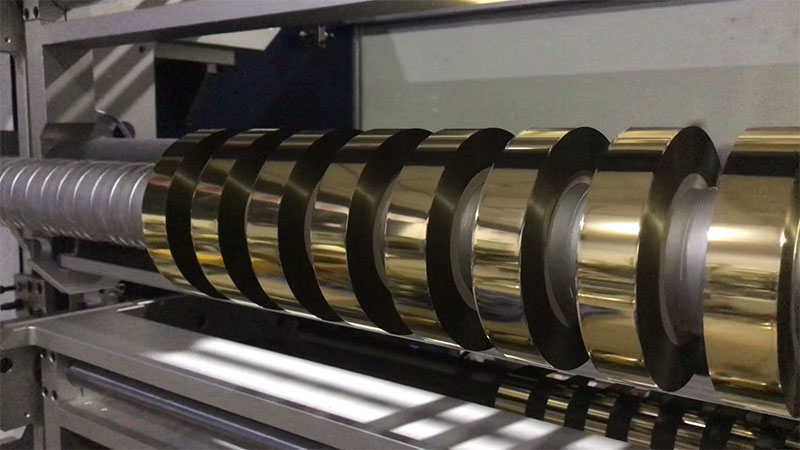
1350mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitting Machine New Energy Ultra-thin Film Slitting Machine For Capacitive Film
New Energy Ultra-thin Film Slitting Machine For Capacitive Film Customerized Slitter
Customerized Slitter 350mm Mini Slittting Machine
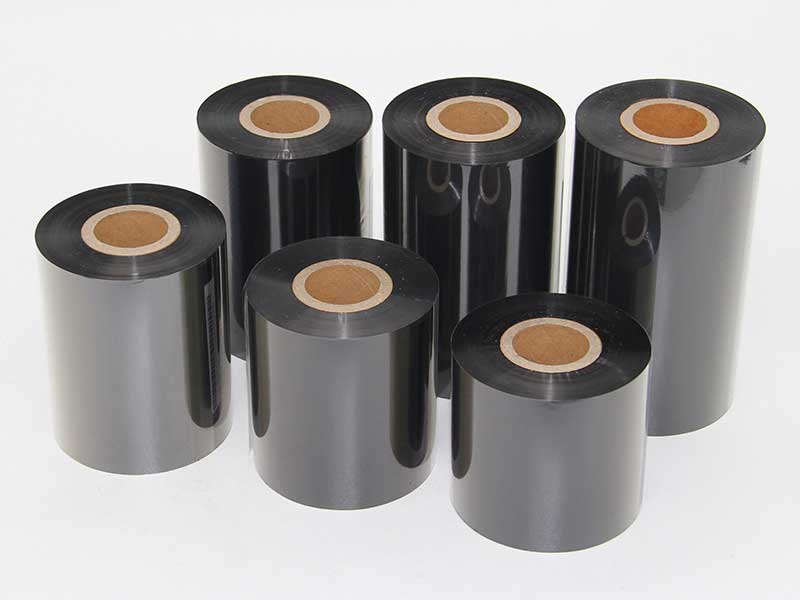
350mm Mini Slittting Machine Barcode Ribbon Slitting Machine
Barcode Ribbon Slitting Machine Label Slitting Machine
Label Slitting Machine