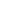
When selecting the slitting machine configuration according to the material thickness (0.02-2mm), it is necessary to comprehensively consider the slitting accuracy, tension control, tool type, equipment rigidity and auxiliary system. Here are some suggestions for specific options:
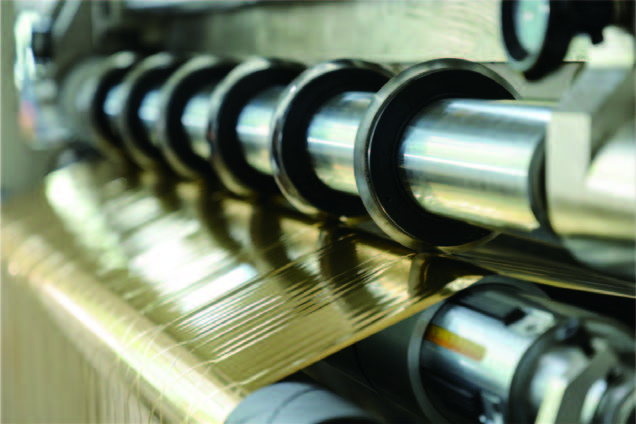

1. Slitter type selection
• Ultra-thin materials (0.02-0.1mm):
◦ Precision round knife slitting machine: Adopt high-precision pneumatic or servo-controlled round knife system to avoid material deformation.
◦ Laser slitting machine: suitable for extremely thin and fragile materials (such as film, copper foil), non-contact cutting, no burrs on the edges.
◦ Configuration requirements: high rigidity frame, micron-level deviation correction system, constant tension control (within 0.5% ±).
• Medium thickness (0.1-1mm):
◦ Flat knife or round knife slitting machine: flat knife is suitable for low-speed and high-precision (such as paper, PET sheet), and round knife is suitable for high-speed continuous slitting (such as plastic, metal foil).
◦ Requirements: servo-driven tools, dynamic tension control (±1%), automatic lubrication system.
• Thicker materials (1-2mm):
◦ Heavy-duty hydraulic slitting machine: Equipped with high-torque motor and hydraulic cutter, it is suitable for hard materials (such as rubber sheets, composite materials).
◦ Configuration requirements: high-power motor (more than 7.5kW), hydraulic or pneumatic pressing device, wear-resistant tools (tungsten steel or ceramic coating).
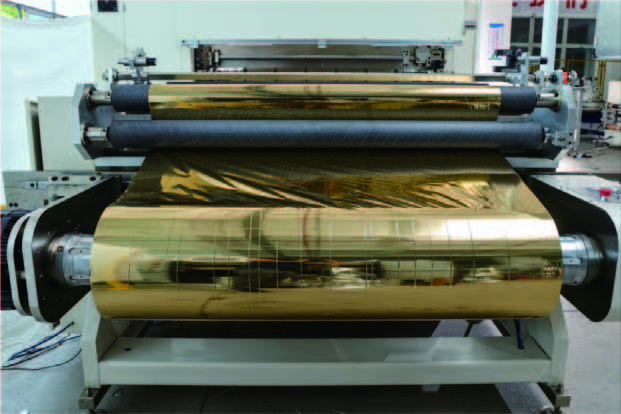

2. Key configuration parameters
• Tool selection:
◦ 0.02-0.5mm: diamond-coated round knife or laser knife with a cutting edge angle of ≤ 30°.
◦ 0.5-2mm: tungsten carbide flat knife or disc knife, cutting edge angle 45°-60°.
• Tension Control:
◦ Ultra-thin material: magnetic particle brake + closed-loop tension controller (accuracy ± 0.1N).
◦ Thick material: inverter motor + floating roller compensation.
• Slitting speed:
◦ Film (0.02mm): 100-300m/min (dust-free environment required)
◦ Thick plate (2mm): 5-20m/min (low speed and high torque).
• Web Guiding System:
◦ Photoelectric guiding (±0.1 mm) is used for transparent films, and ultrasonic guidance is used for opaque materials.
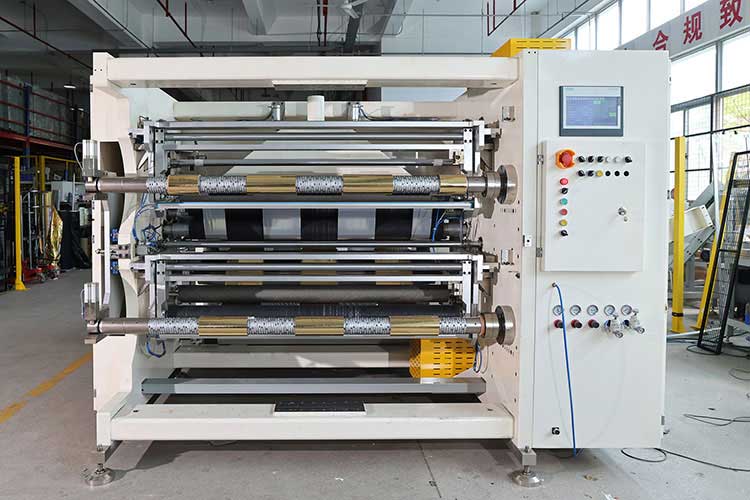

3. Adaptation of material properties
• Ductile materials (e.g. PE film): low-temperature slitting (with cooling rollers), low tension.
• Brittle materials (e.g. fiberglass): High-frequency vibrating tools reduce chipping.
• Adhesive materials (e.g. adhesive tape): anti-stick coated guide rollers, in-place cleaning device.
4. Additional feature suggestions
• 0.02-0.1mm:
◦ Static eliminator, dust-free take-up system.
• 1-2mm:
◦ Automatic scrap recycling, tool wear monitoring.
Configuration example
• Slitting 0.03mm foil:
◦ Laser slitting machine + air bearing guide roller + constant temperature workshop (±1°C).
• Slitting 1.5mm silicone sheet:
◦ Hydraulic flat knife slitting machine + 20 tons of pressing force + infrared edge system.
By matching the thickness of the material with the rigidity, precision and dynamic control ability of the slitting machine, problems such as slitting burrs, wavy edges or material stretching can be avoided to the greatest extent. It is advisable to perform a sample test first to optimize the parameters (e.g. tension gradient, tool clearance).
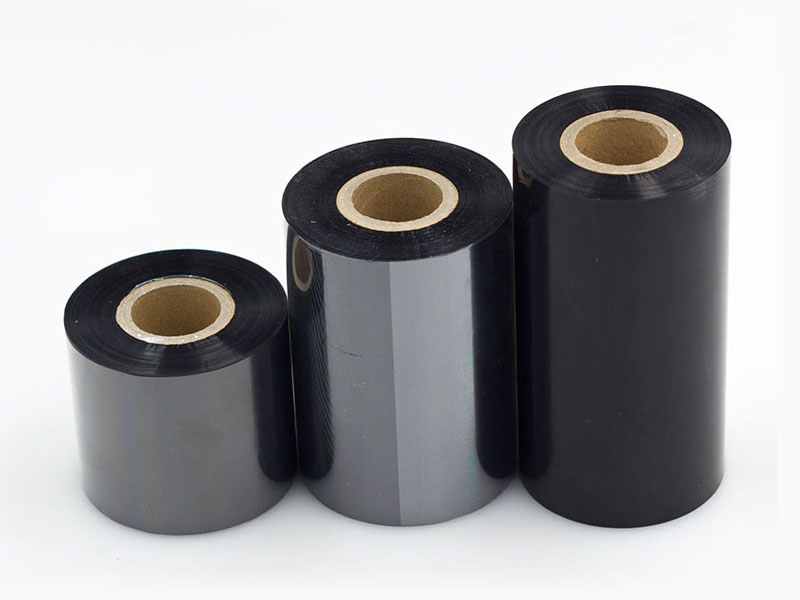
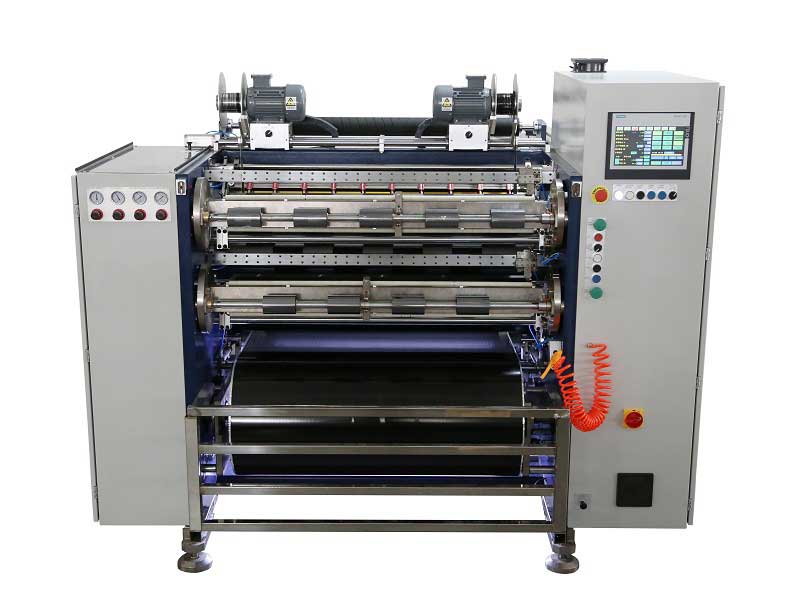




 Automatic Thermal Transfer Ribbon Slitting Machine RSDS8 H PLUS
Automatic Thermal Transfer Ribbon Slitting Machine RSDS8 H PLUS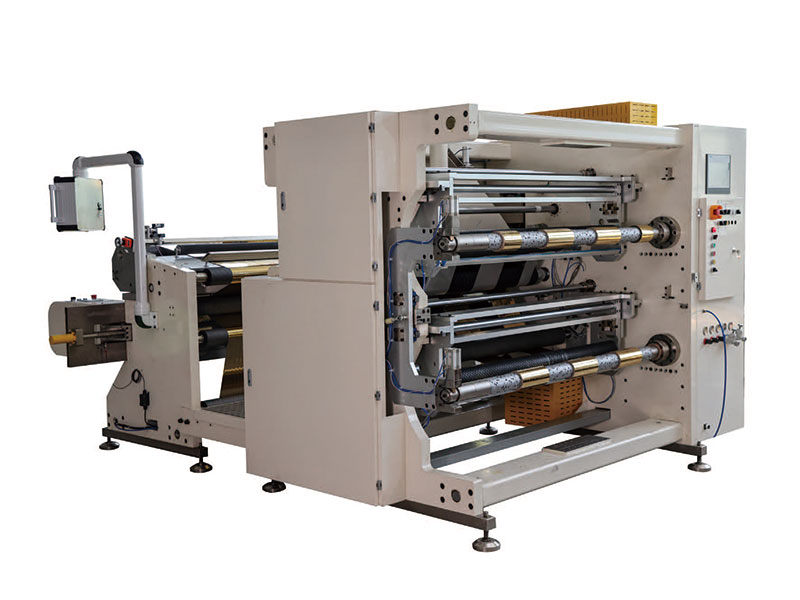 1400mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitting Machine
1400mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitting Machine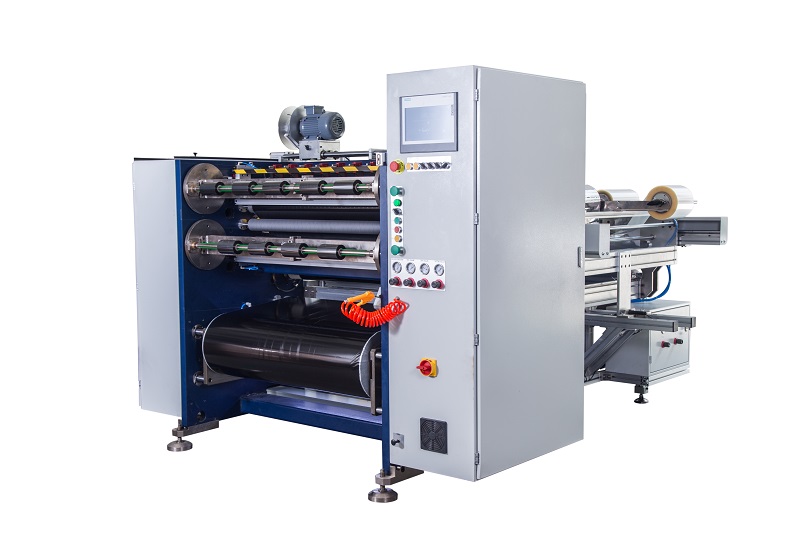 Semi Automatic Thermal Transfer Ribbon Slitting Machine RSDS5 PLUS
Semi Automatic Thermal Transfer Ribbon Slitting Machine RSDS5 PLUS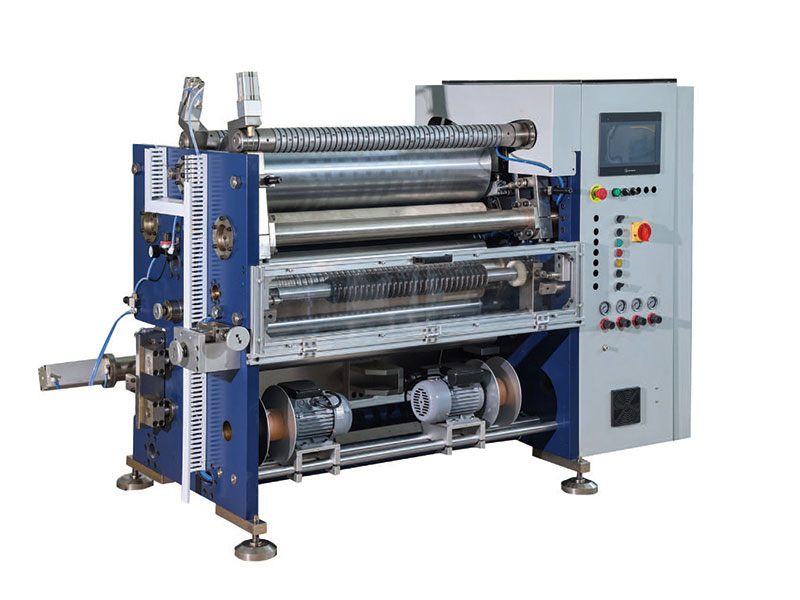 800mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitting Machine
800mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitting Machine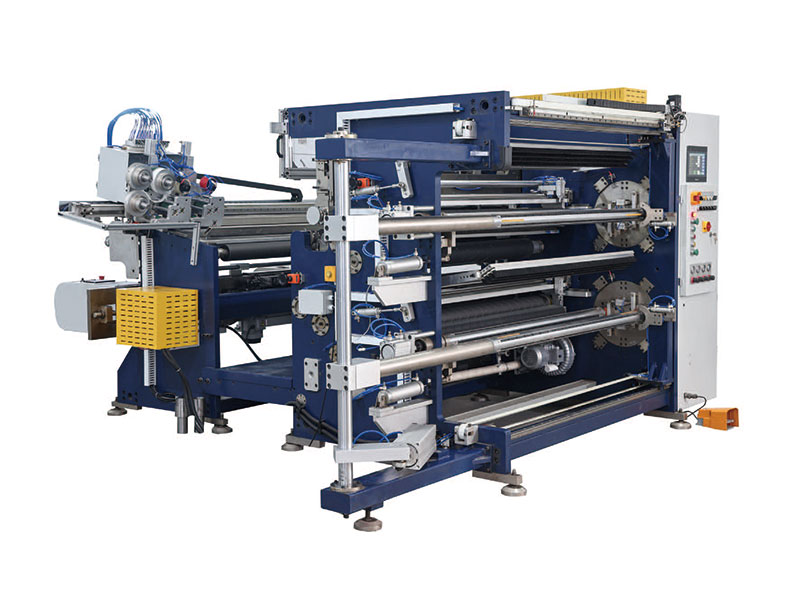 1350mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitting Machine
1350mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitting Machine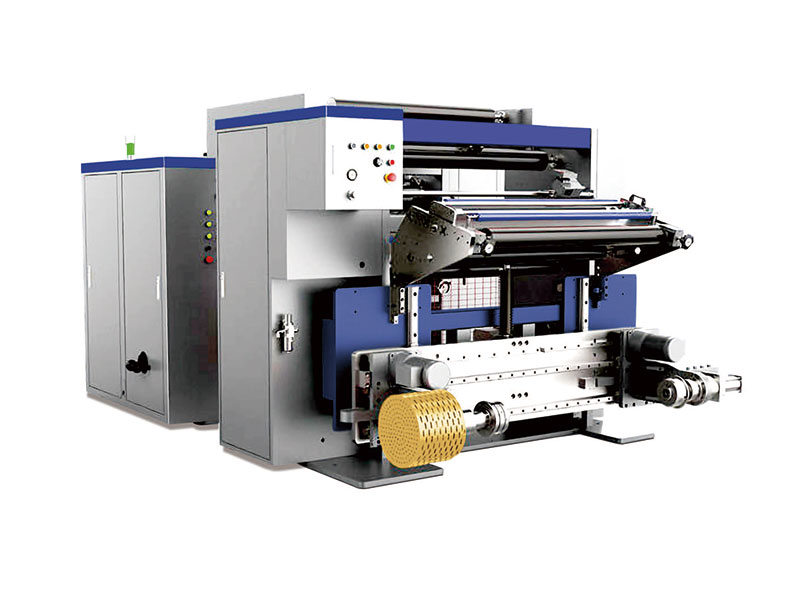 High Speed Slitting Machine
High Speed Slitting Machine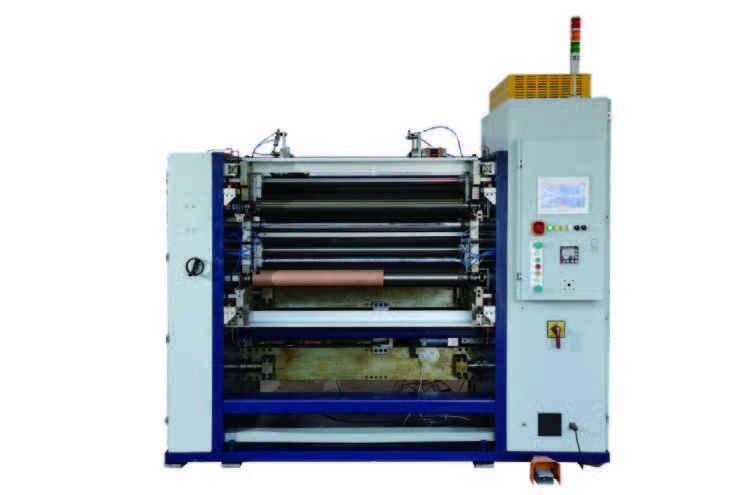 New Energy Ultra-thin Film Slitting Machine For Capacitive Film
New Energy Ultra-thin Film Slitting Machine For Capacitive Film Customerized Slitter
Customerized Slitter