Choosing the right film slitting machine requires a comprehensive consideration of the following 5 key parameters to ensure that the equipment matches the production needs, material characteristics and process requirements:

1. Slitting width range
• Core requirements: Determine the maximum and minimum slitting width of the slitter according to the product specifications.
• Notes:
◦ The equipment needs to support stepless adjustment or fixed tool position to adapt to different widths of film (such as BOPP, PET, PE, etc.).
◦ High-precision slitting (within ±0.1mm) requires servo drive or digital control system.
• Example: If you need to cut a film of 0.5m~2m, the selection range needs to be slightly larger than this (e.g. 0.3m~2.2m) to leave a margin.
2. Slitting speed and production efficiency
• Key indicators: Slitting speed (usually 50~1000 m/min) directly affects the output.
• Matching Factors:
◦ Film material (e.g., CPP low-speed slitting and anti-stretch, metallized film needs to be high-speed).
◦ Number of winding stations (double stations reduce downtime and increase efficiency).
• Recommendation: Choose a model that is 20% faster than your current needs and have room for future upgrades.

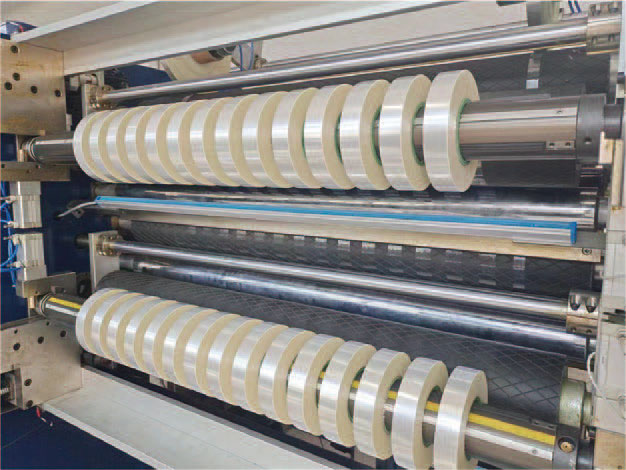
3. Tension control accuracy
• Importance: Affects the flatness, end-face uniformity and material properties of the coil after slitting.
• Technical solutions:
◦ Magnetic particle brake (economical, suitable for low speeds).
◦ Servo tension control system (± 0.5% accuracy, suitable for high-tensile films such as lithium battery separators).
• Test points: Observe for serpentine rolls, edge breaks, or slack during slitting.
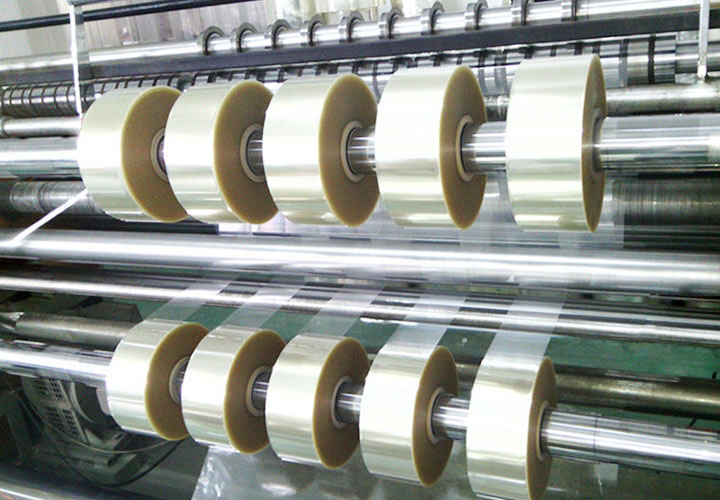
4. Rewinding and unwinding diameter and bearing capacity
• Parameter matching:
◦ Unwinding diameter (usually 600~1500mm), need to match the size of the raw material roll.
◦ Rewinding diameter (limited by equipment structure, such as inflatable bearing load 3~5T).
• Scalability: Automatic roll changing, online monitoring system can reduce manual intervention.
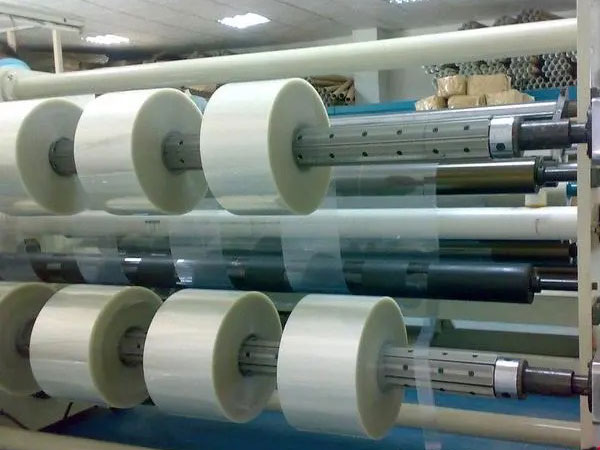

5. Slitting method and tool configuration
• Selection Basis:
◦ Blade slitting: suitable for rigid film (such as PET), pay attention to the tool material (tungsten steel/ceramic) and life.
◦ Shearing and slitting: used for elastic films (such as PE) to reduce burrs.
◦ Laser slitting: High precision is required (e.g., optical film), but the cost is higher.
• Additional features: dust removal device, online defect detection can improve the yield rate.
Other factors to consider:
• Degree of automation: automatic edge alignment, waste side suction and other functions can reduce labor costs.
• Brand and after-sales: Priority is given to manufacturers with mature cases.
• Energy consumption vs. maintenance: Compare long-term costs such as equipment power, lubrication system design, etc.
Summary: Balance the above parameters according to the type of film (e.g., thickness, ductility), production scale (batch/small batch) and accuracy requirements, and verify the actual effect through equipment testing. It is recommended to list the priorities (such as speed> accuracy, > cost) and then filter the models by type.
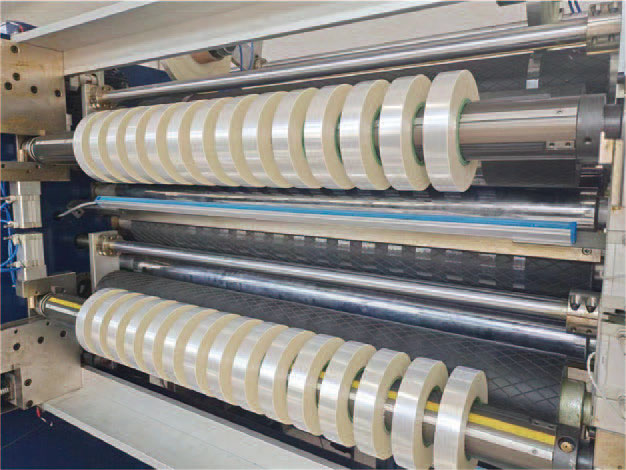
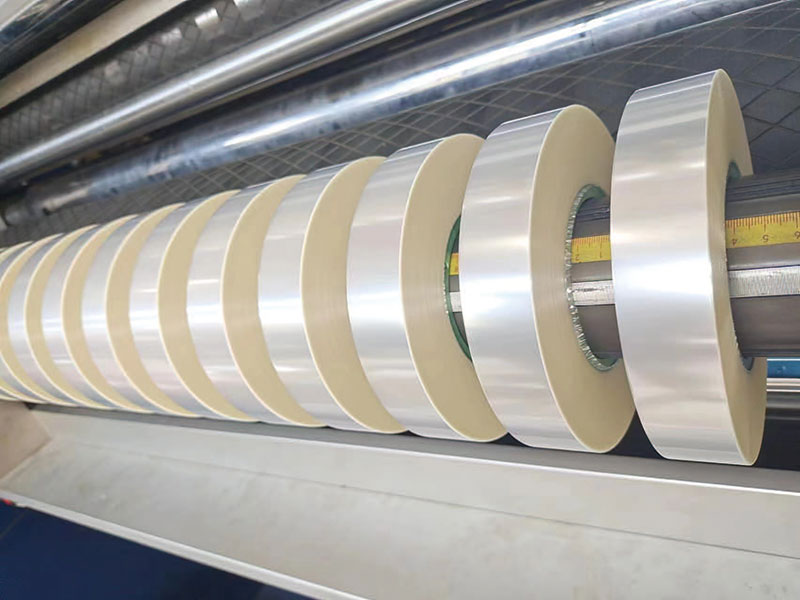
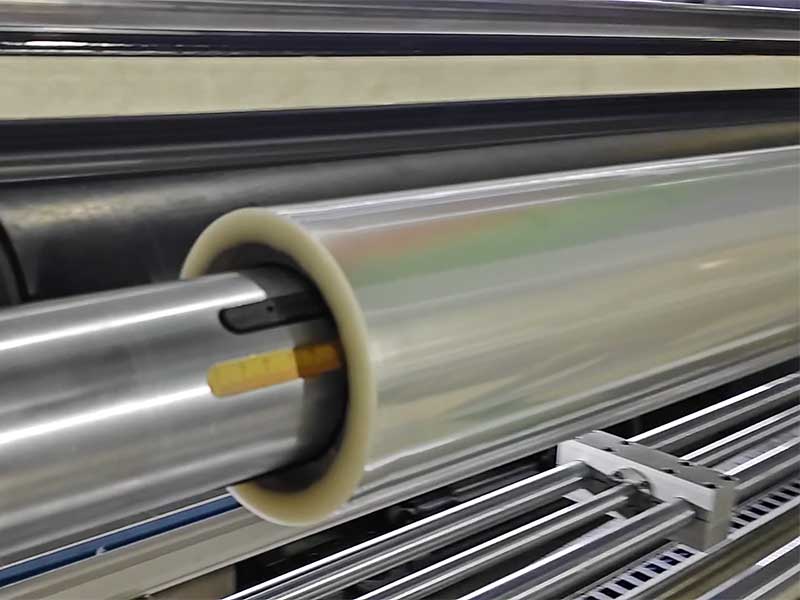
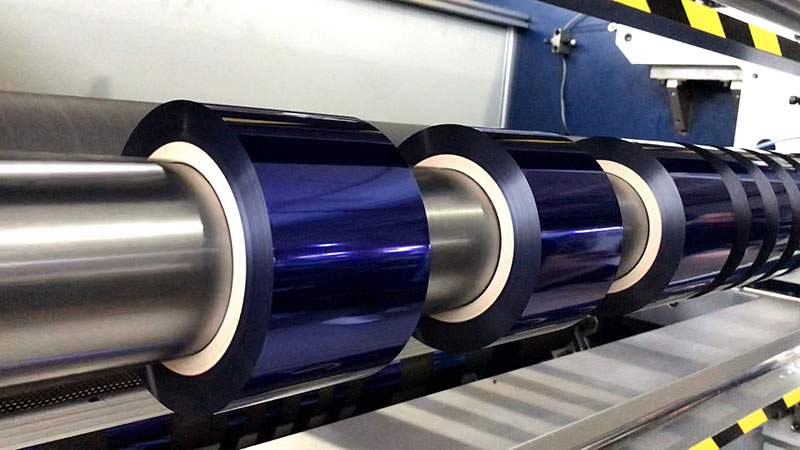
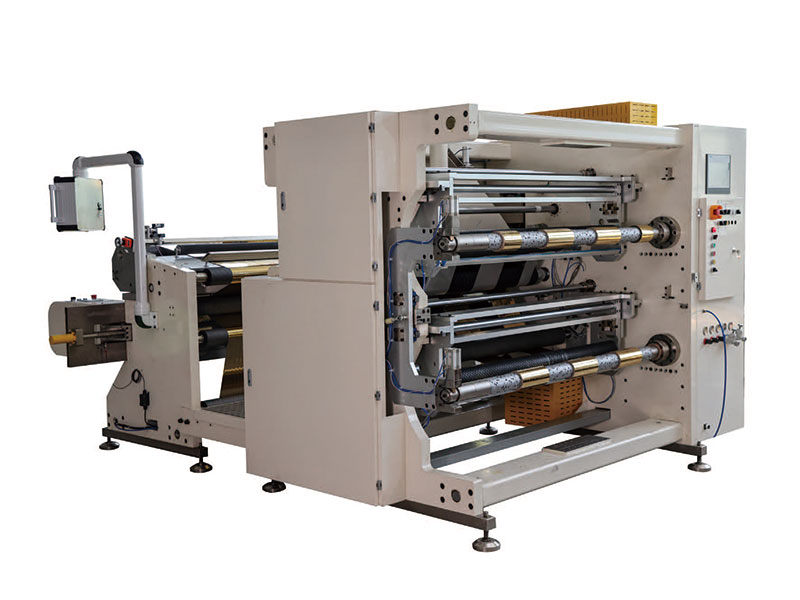






 1400mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitting Machine
1400mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitting Machine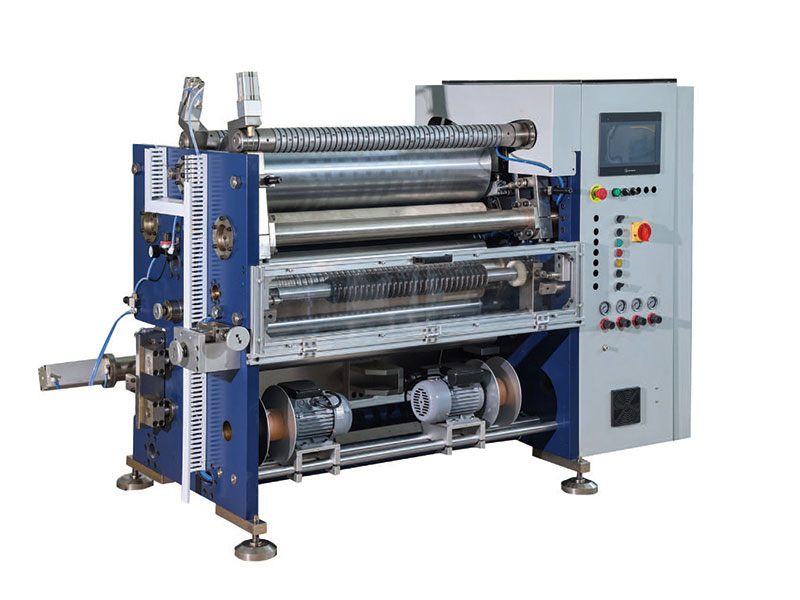 800mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitting Machine
800mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitting Machine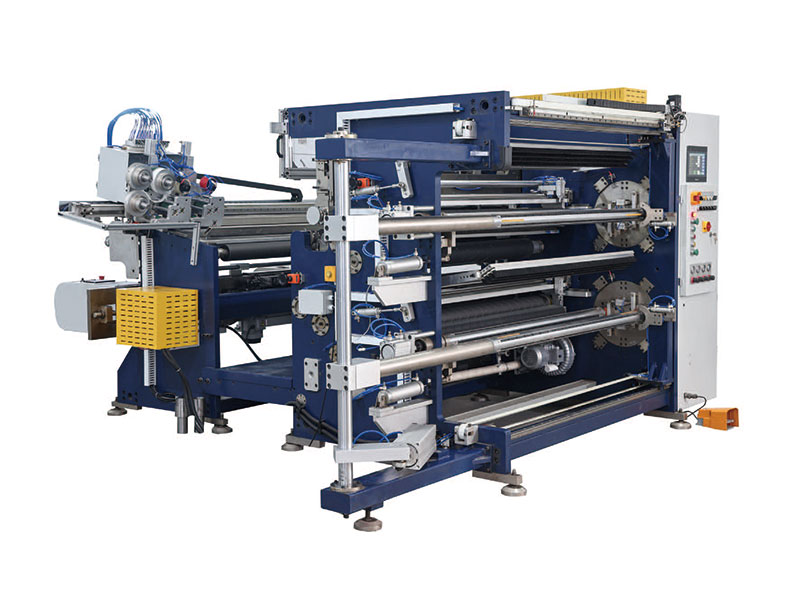 1350mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitting Machine
1350mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitting Machine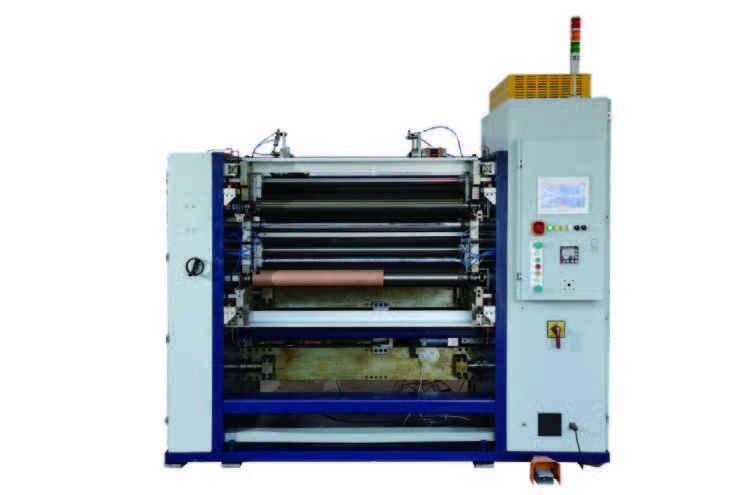 New Energy Ultra-thin Film Slitting Machine For Capacitive Film
New Energy Ultra-thin Film Slitting Machine For Capacitive Film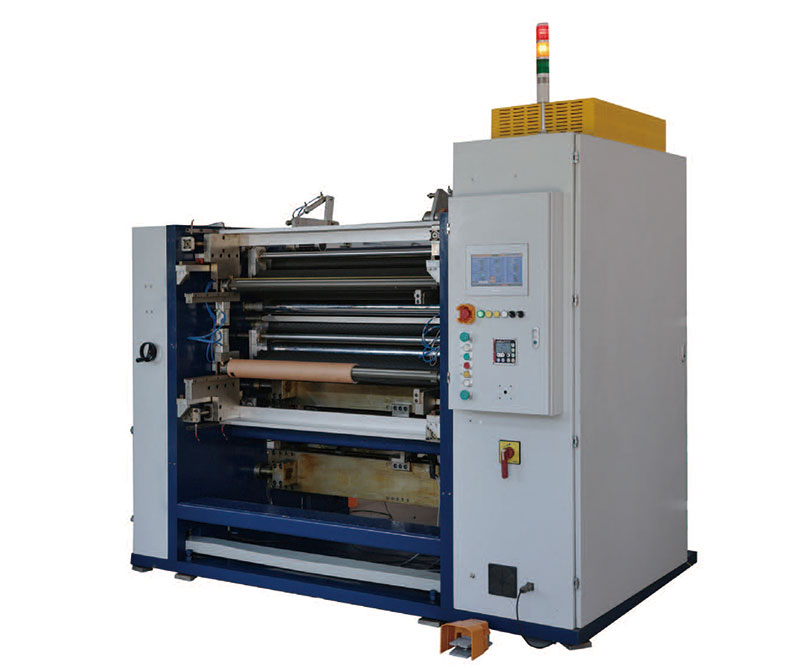 New Energy Ultra-thin Film Slitting Machine For MOPP
New Energy Ultra-thin Film Slitting Machine For MOPP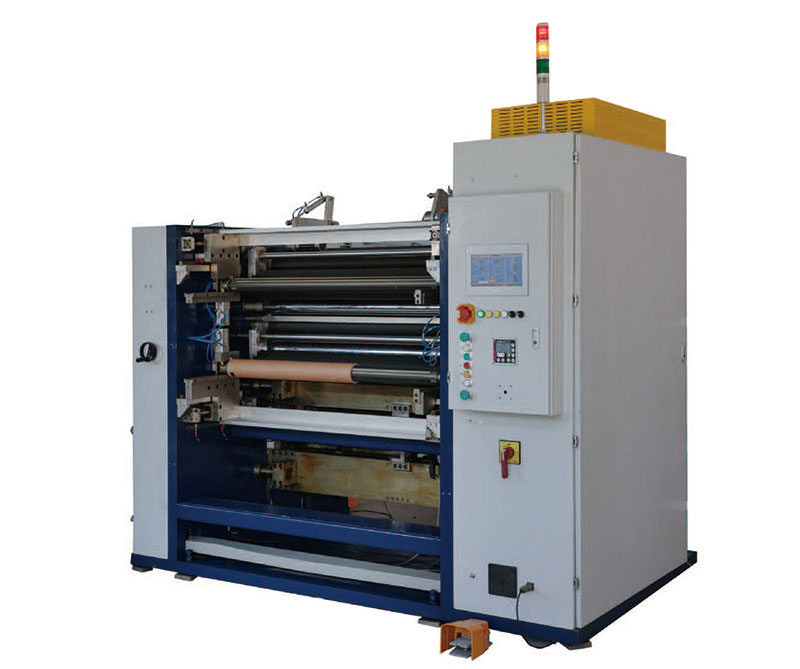 New Energy Ultra-thin Film Slitting Machine For MPET
New Energy Ultra-thin Film Slitting Machine For MPET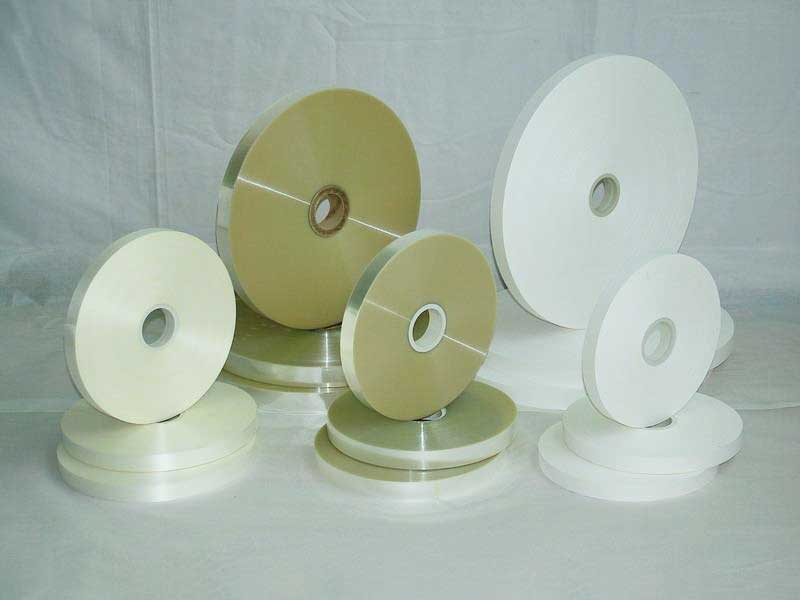 Film Slitting Machine
Film Slitting Machine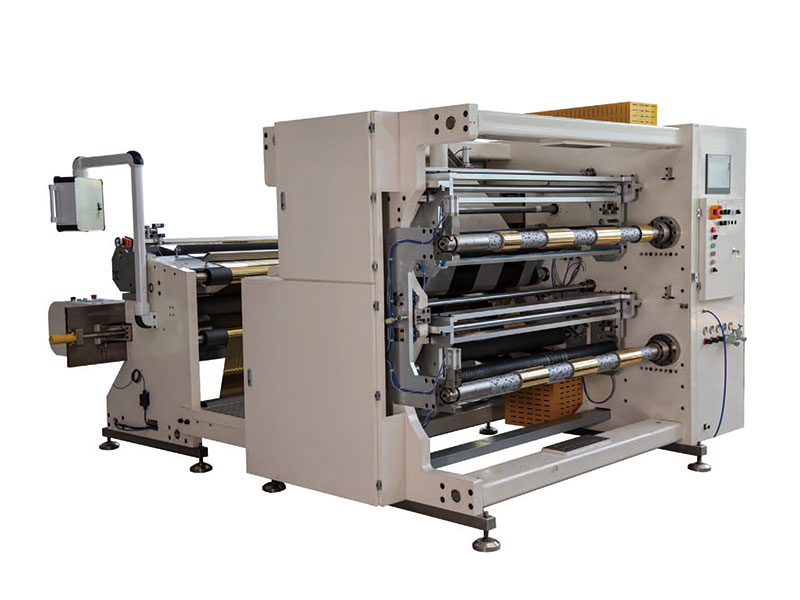 1400mm Copper Foil Slitting Machine
1400mm Copper Foil Slitting Machine